Benefits
How it’s cleaner
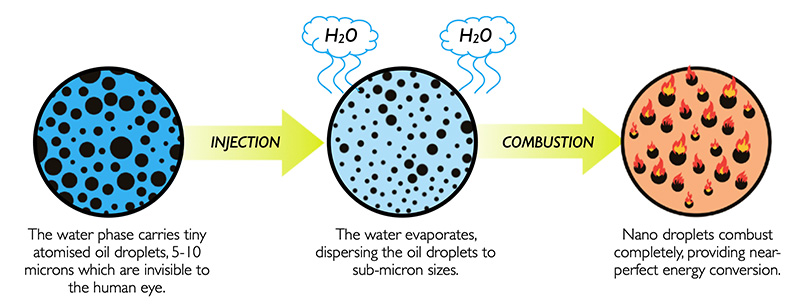
Both MSAR® and bioMSAR™ are water-based fuels and biofuels respectively. The superfine dispersion of oil-soluble droplets (5-10 microns) in the water phase is much smaller than atomised HFO droplets (100 microns). This means that MSAR® and bioMSAR™ have a far greater surface area, enabling complete combustion. All of the fuel is converted to energy. The inherent water within MSAR® and bioMSAR™ also reduces the temperature of combustion, which reduces NOx emissions by up to 45%*, with no visible black soot.
MSAR® delivers up to 9%* reduction in carbon dioxide, and bioMSAR™ offers over 20% reduction in emissions compared to HFO. This is comparable with LNG use, but without the risk of methane slip, which is 21 times worse than CO2 as a greenhouse gas.
See how bioMSAR™ burns cleaner compared to diesel. The images are from the latest testing on our 40kW Cummins diesel generator. On the left is road diesel and on the right is bioMSAR™ at the same conditions.

How it’s cheaper
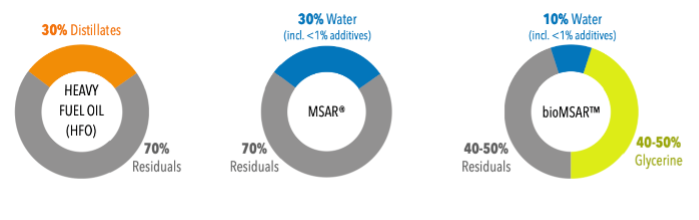
Where a refinery produces heavy fuel oil (HFO), some higher value distillate or ‘cutter stock’ is diverted and downgraded to the fuel oil pool to dilute the residues. In simple terms, the heavier the crude or the more complex the refining process, the more distillate requirement per ton of residual oil.
Both MSAR® and bioMSAR™ fuel take the most viscous refinery residues, the lowest value fraction of the barrel, without any of the high value distillates.
Our technology replaces these high-value distillates with lower-cost water (even waste water) and <1% of additives, thereby improving a refinery’s conversion of a barrel of oil into premium-value products by 10-20%.
The economics of the MSAR® technology solution enable the refinery to obtain a premium residual oil value, whilst still allowing the MSAR® to be sold at a discount to HFO to incentivise and attract end-users.
Compared to fuel oil, MSAR® delivers a savings over 10%. bioMSAR™ takes this one step further, displacing some of the fossil fuel with renewable biofuels such as glycerine. Compared with similar biofuels, bioMSAR™ delivers a saving over 10% per unit energy.
bioMSAR™ production can be considered as a standalone option or an add on to conventional MSAR® production; both are produced in a similar manner, utilising the same MSAR® technology and process equipment.
MSAR® and bioMSAR™ are interchangeable and compatible with each other, and our future net-zero solution bioMSAR Zero will offer similar compatibility benefits.
How it’s simpler
Quadrise’s technology is modular and can be integrated for production in under 12 months, without incurring significant capital expenditure which differentiates Quadrise’s technology from alternative heavy oil and biofuel upgrading solutions.
By comparison, an LNG conversion requires new, highly expensive cryogenic storage and liquefaction systems. In comparison, bioMSAR™ can be implemented cheaply using existing HFO infrastructure. Our blending systems are modular and scaleable, to allow installation on vessels, refineries or power plants («blend-on-board/site»).
Both MSAR® and bioMSAR™ fuels use existing HFO logistics infrastructure, hence are ‘drop-in’ solutions. They are compatible with each other, and with products from different refineries.
How it’s safer
Both MSAR® and bioMSAR™ are extremely stable, with storage and handling possible at much lower temperatures than HFO. As emulsion fuels, MSAR® and bioMSAR™ both readily disperse in water in the unlikely event of a spill; a characteristic which is different to conventional HFO or biofuels. As non-volatile and biodegradeable products, MSAR® and bioMSAR™ pose minimal risk to staff who are handling these products.
How it’s different
Our Oil-in-water emulsion fuels are different from Water-in-oil emulsions (WIO, also called water-in-fuel or WIF).
WIO emulsion fuel technologies are installed at the point of use and add typically 10-15% water and sometimes additives to conventional fuels, such as HFO, VLSFO or diesel. Small water droplets are suspended in the oil to promote secondary combustion as the water evaporates. The main drivers for such systems are emissions reductions of NOx and PM and claimed improvements to fuel efficiencies that may offset the system cost installed on the vessel or power plant. WIO emulsion stability is variable depending on the mixing system and additives used.
Water concentrations of over 10% in WIO systems can lead to increasing fuel viscosity requiring higher fuel temperatures and pressures as a result. In diesel engines, fuel oil consumption generally gets worse when 15% or more of water is added to WIO emulsions, as the fuel with high viscosity is injected after the optimum time in the diesel cycle, leading to incomplete combustion. This phenomenon effectively limits the amount of water that can be added (to 10-15%), as well as any water-based biofuels to limit GHG emissions in the future.
By contrast MSAR® technology produces a stable OIW (or fuel-in-water, FIW) emulsion where 5-10 micron-sized oil droplets are suspended in water or a water-based biofuel that acts as a “carrier” liquid.
This system reduces the fuel viscosity to an optimum level of <180cSt at 50°C which is lower than HFO, even when very high viscosity oils, residues or bio-oils are used to reduce the cost of energy. The lower OIW fuel viscosity permits more fuel to be injected over a shorter time, and the micron oil/bio-oil droplets of the fuel combusts more rapidly than WIO emulsions or standard fuels.
The MSAR® system allows for over 25% water or water-based biofuels to be added, reducing fuel consumption and emissions of NOx, PM and importantly GHGs.
In simple terms for WIO emulsions, think butter or whipped cream; for OIW emulsions think milk or mayonnaise. Underneath they’re both a blend of oil and water, but OIW emulsions are more fluid.
Tested and proven
Both MSAR® and bioMSAR™ emulsion fuels have been proven at commercial scale, for further details please read our References for bioMSAR™ and for Specifications please refer to the comparison table with ISO8217 fuels below.


